The VIKI smart home is an unique artificial intelligence system that reduces your energy bill by 30%. After implementing and tracking energy consumption in the first location, we were able to confirm that the automation of a house is not only about comfort and security, but also about reducing costs, due to the savings on electricity and heat.
Here are some examples of devices that can be connected to VIKI, the “butler” of the house, which are controlled to save energy:
Thermostats for the central heating boiler
The thermostat connected to VIKI prevents the boiler to start when it is not necessary. It also prepares the house with the optimal desired temperature for the moment when you get home.
Such a thermostat allows remote control of the house climate, through the VIKI application. You can choose the “Coming home” scenario, and it will send commands to all devices involved, so that on arrival you can enjoy the temperature you are used to.
In addition, when you leave home and forget an open window, if you have a door-window sensor installed, it will transmit the message to VIKI, which will implicitly order the thermostat to turn off the boiler or operate at minimum capacity, preventing any additional costs.
A house with many rooms can have high heating costs, but if it is well insulated, through the intelligent control of the house you can get an effective program to reduce the flow of heat by reducing the heating of unused rooms. For example, during the night, VIKI knows which rooms are empty and will adjust the temperature. And by day, when the house is empty, when selecting the “Leave” scenario, VIKI will switch to the minimum resources consumption mode. The same goes when you leave for the weekend or on longer vacations.
When choosing the “Weekend” scenario, VIKI will keep the house temperature at 17 degrees. And if you choose the “Holiday” scenario, then VIKI will know how to keep the house temperature at 16 degrees. And if it’s summer, VIKI will not turn on the ventilation or air conditioning systems only after a certain temperature, for example 32 degrees Celsius.
Smart lighting and switches
Once the main sockets and switches have been optimized with intelligent systems, they communicate with VIKI and are able to use exactly as much energy as needed, with minimal losses even when you forget the light on. VIKI learns user behavior and then everything happens automatically, the lights come on when you enter a darker room and go out when the user leaves the room or house.
The automated sockets in this system work the same way – VIKI will turn on the lamp when it detects low light and then turn it off when the user leaves the room.
Multimedia
In the absence of users, VIKI will communicate with the TV or audio system by turning it off; or it will turn it on the specific channel according to the preferences of the users in the room.
Automation of the windows blinds
Another smart way to save money is to automate blinds. After learning the user’s behavior, VIKI will automatically open the blinds in the morning and will leave them at sunset, thus taking full advantage of natural light, without the need for artificial lighting. This scenario can be simulated even when you leave the house, thus saving heat; the house is partially heated by the sun, but will also have a protective role in the absence of owners simulating the same behavior daily.
The VIKI team monitored the energy consumption in a pilot project (72 sqm apartment) progressively implemented since 2014, and the result was a reduction of up to 30% in consumption, as shown in the graph below:
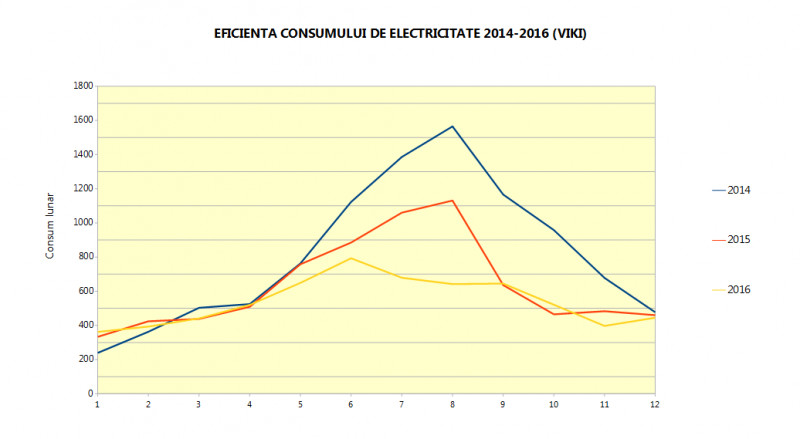
Managing electrical equipment and air conditioning systems installed in a smart home will bring significant long-term savings. Even if it’s only a few degrees more in winter or less in summer, they can substantially reduce gas and electricity bills.
